Description
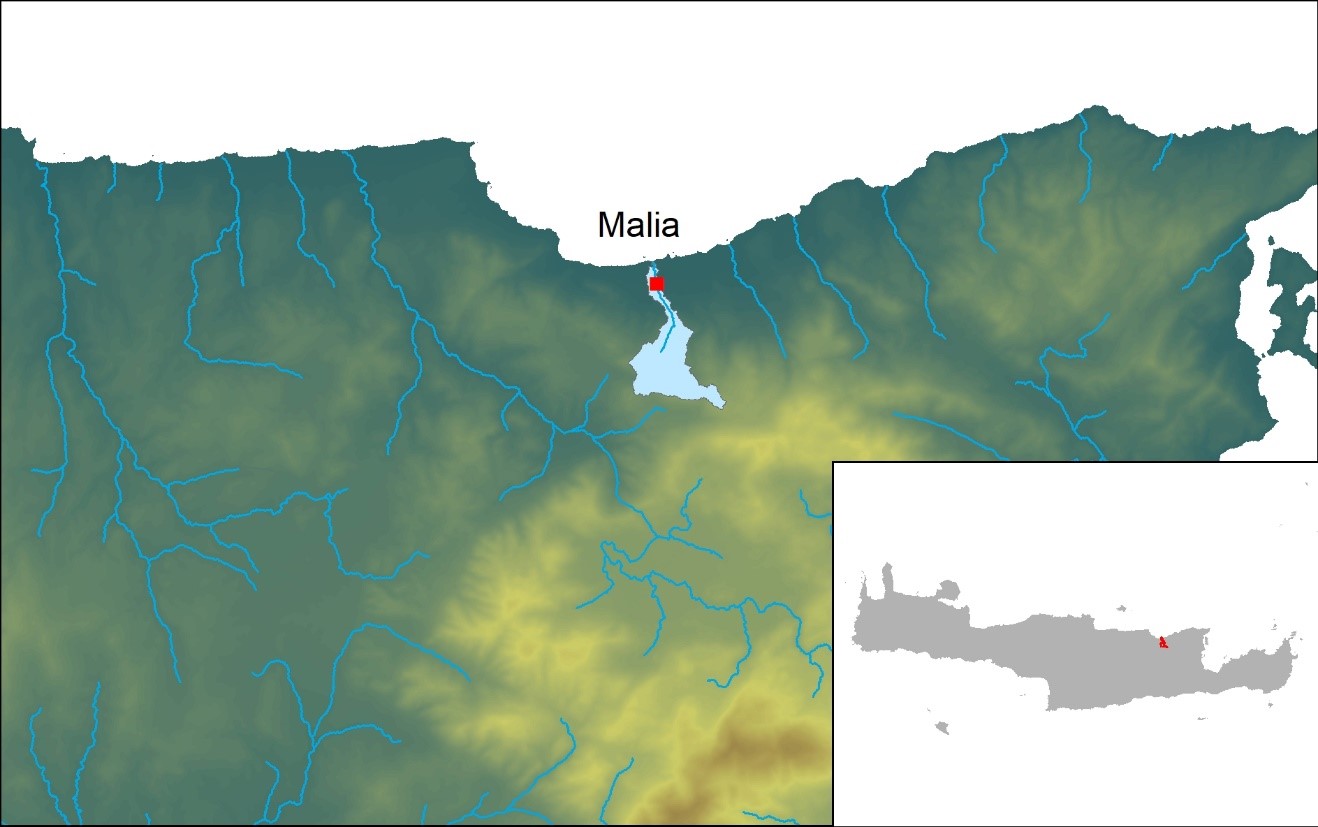
The catchment of Malia is located in northern Crete, Greece, 40 km east of the city of Heraklion. The study area is characterized by a gentle slope to the north of the town of Malia and by mountains to the south. The elevation varies from 0 to 200 m above mean sea level (amsl) over the coastal lowland and from 200 to 550 m amsl over the area south of the city of Malia and towards the south. The cultivated area of the municipality of Malia is 1.75 km2. Sclerophyllous vegetation and complex cultivation patterns cover most of the study area. Other land uses include olive groves, natural grassland, non-irrigated arable land and a small area of discontinued urban fabric around the town of Malia.
The coastal karstic aquifer of Malia is developed in limestones of the Tripolis zone. Under these rocks, a series of alternating chloritic schists, phyllites and quartzites belonging to the Phyllite-Quartzite zone acts as the impermeable substrate of the extended region. The Tripolis series consists of faulted and karstified limestones, dolomites and calcareous dolomites (Jurassic-Critidic and Triassic-Jurassic). The stratigraphy includes Neogene deposits that consist of bioclastic Messinian limestones and Quaternary clastic sediments. Along the coast, alluvial deposits and beach sand deposits are found (Quaternary deposits).
Specific problems
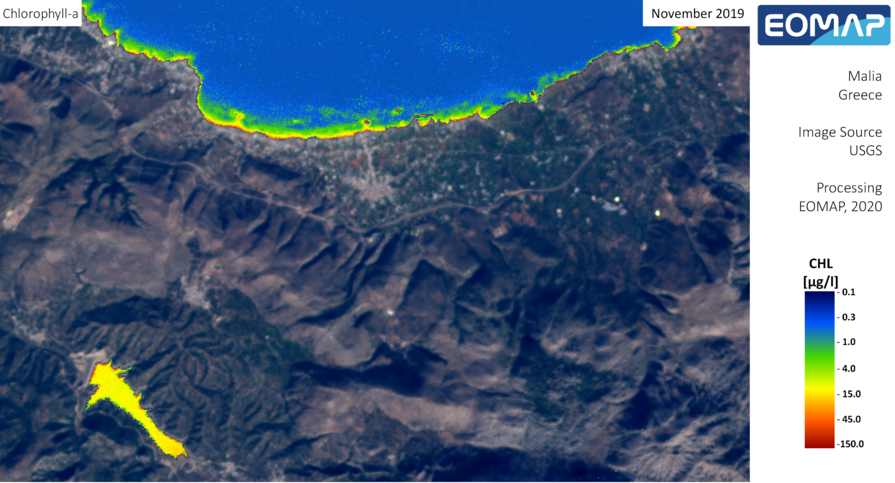
Surface water and groundwater are used to support the extensive agricultural activity in the area, while the last 20 years the increased touristic development has raised significant water consumption demands. The water resources in the area are very important for its residents as they cover their drinking water needs as well as their welfare depends from the agricultural and touristic activities that consume large amounts of water. Thus, groundwater level been significantly depleted the last 30 year causing extensive groundwater salt water intrusion.
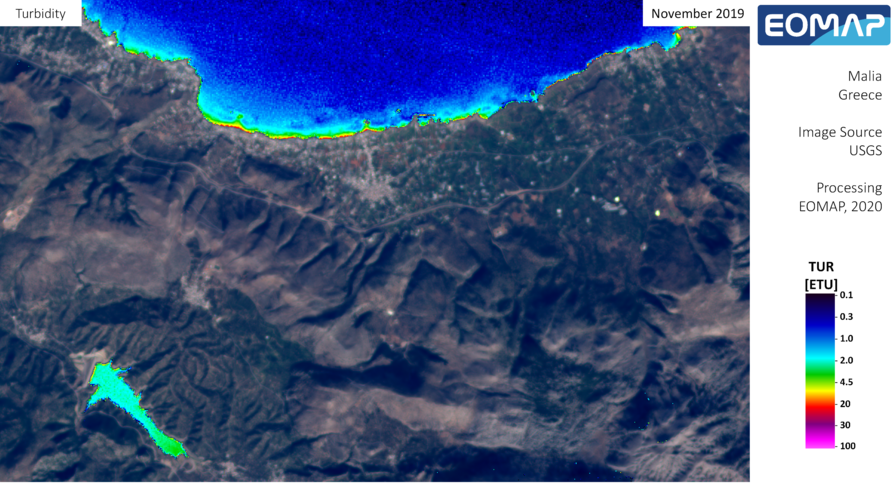
The water quality in the area has been significantly depleted due to extensive salt water intrusion of the aquifer. Therefore high Cl- concentrations are found in groundwater which in conjunction with over-pumping result to low aquifer levels and groundwater degradation. In addition, increased nitrates concentrations are also found in groundwater due to the extensive agricultural activity in the area.
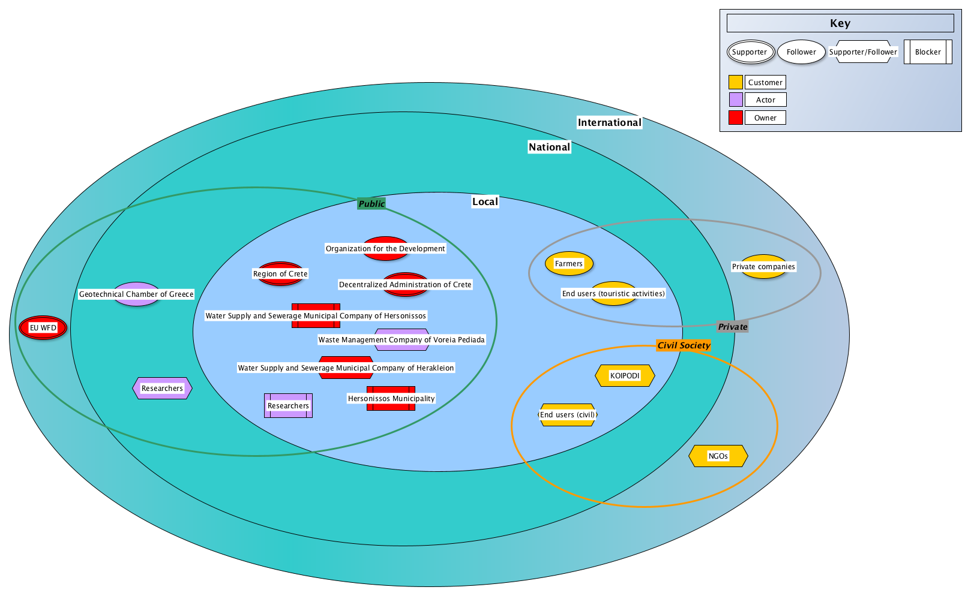
List of stakeholders
- Waste Management Company of Voreia Pediada
- Decentralized Administration of Crete
- Directorate of Water
- Region of CRETE
- Organization for the Development of Crete S.A.
- Hersonissos Municipality
- Social Ecological Cultural Network Associations of Hersonissos Municipality (KOIPODI)
Map